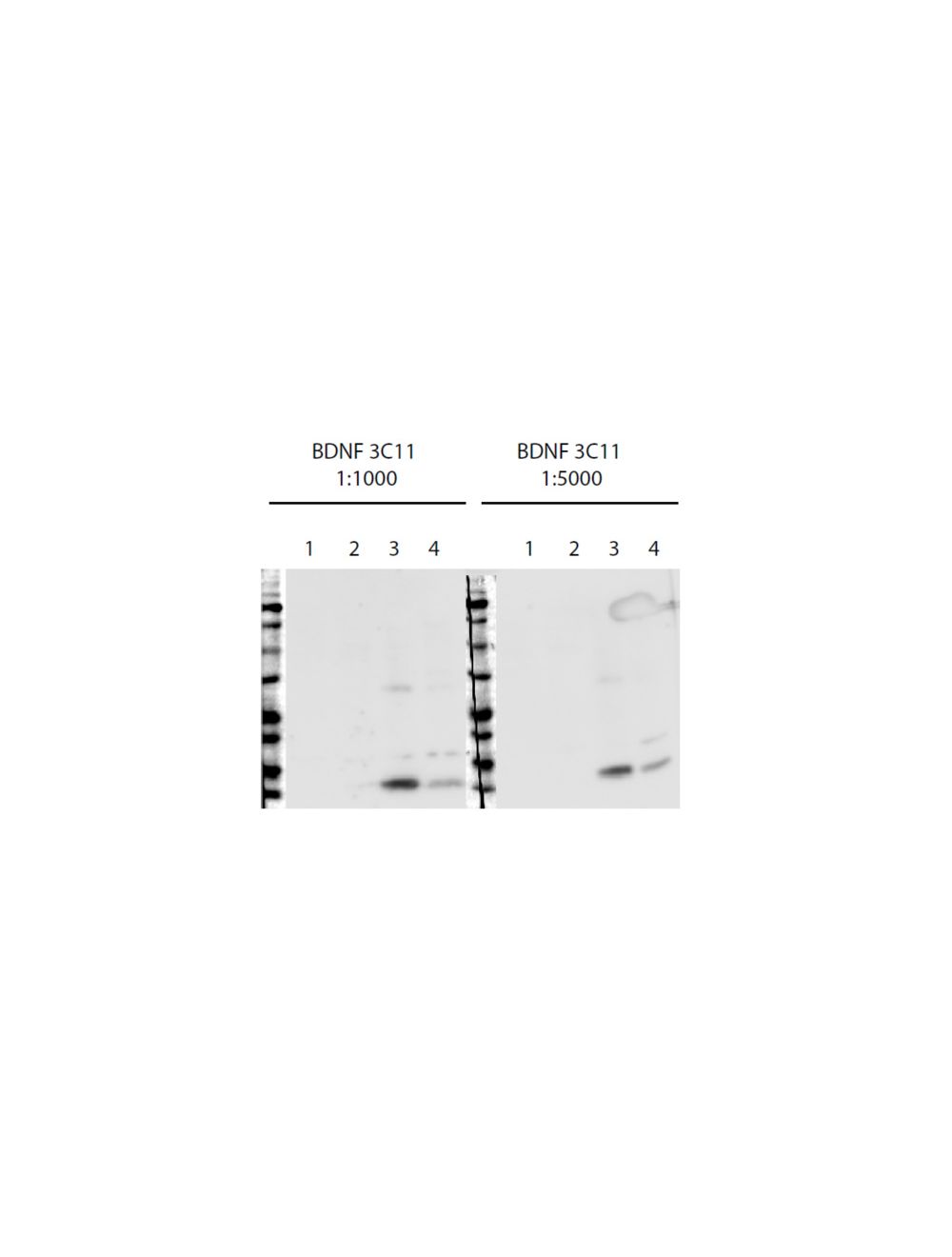
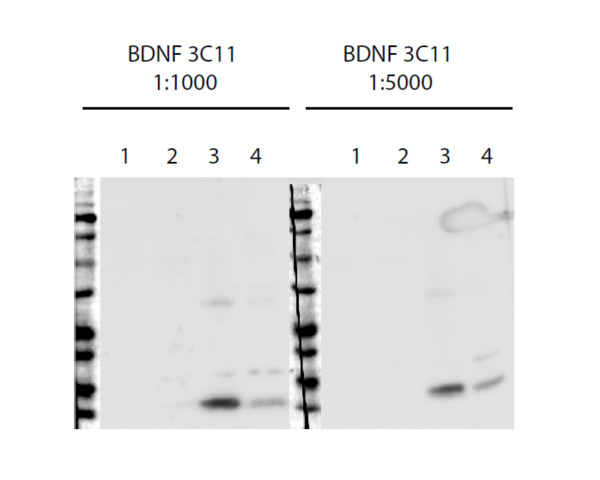
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
As low as
US$253.00
Only %1 left
Catalog Number
M-1736
- Product Name Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
-
Product Description
Mouse anti-Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Monoclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for ELISA, WB, ICC.
- Alternative Names Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Abrineurin; proBDNF
- Application(s) ELISA, ICC, WB
- Antibody Host Mouse
- Antibody Type Monoclonal
- Specificity Detects human, mouse, rat, guinea pig BDNF. Expected to detect BDNF from other species due to sequence homology.
- Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Rat
- Immunogen Description Recombinant human mature BDNF expressed in E.coli
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Purity Description Protein G purified mouse IgG.
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Product Info
-
Product Description
Mouse anti-Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Monoclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for ELISA, WB, ICC.
- Application(s) ELISA, ICC, WB
- Application Details ELISA (50-100 ng/mL), WB (0.2 to 2 µg/mL), IF (2 to 20 µg/mL). Biosensis recommends optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- Target Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
- Specificity Detects human, mouse, rat, guinea pig BDNF. Expected to detect BDNF from other species due to sequence homology.
- Target Host Species Human
- Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Rat
- Antibody Host Mouse
- Antibody Type Monoclonal
- Antibody Isotype IgG
- Clone Name 3C11
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Immunogen Description Recombinant human mature BDNF expressed in E.coli
- Purity Description Protein G purified mouse IgG.
- Format Lyophilized from a solution containing PBS pH 7.4, 3% trehalose, with 0.1% sodium azide.
- Reconstitution Instructions Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute with 50 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water to obtain a concentration of 1 mg/mL. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material.
- Storage Instructions Store lyophilized antibody at -20°C to -80°C protected from moisture. After reconstitution divide antibody into useful aliquots and keep aliquots at -20°C to -80°C for a higher stability. Working aliquots can be kept at 2-8°C for up to 1 month. Avoid repetitive freeze/thaw cycles.
- Batch Number Please see item label.
- Expiration Date 12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
- Alternative Names Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Abrineurin; proBDNF
- Uniprot Number P23560
- Uniprot Number/Name P23560 (BDNF_HUMAN)
- Scientific Background BDNF belongs to the neurotrophin family and promotes the survival of neuronal populations that are all located either in the central nervous system or directly connected to it. It is a major regulator of synaptic transmission and plasticity at adult synapses in many regions of the CNS. The versatility of BDNF is emphasized by its contribution to a range of adaptive neuronal responses including long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD), certain forms of short-term synaptic plasticity, as well as homeostatic regulation of intrinsic neuronal excitability. The alterations in BDNF expression induced by various kinds of brain insult including stress, ischemia, seizure activity and hypoglycemia, may contribute to some pathologies such as depression, epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's disease. Microglia release BDNF that may contribute to neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. SUBUNIT: Monomers and homodimers. Binds to NTRK2/TRKB. SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Secreted protein. POst translation modification: Converted into mature BDNF by plasmin (PLG). SIMILARITY: Belongs to the NGF-beta family.
- Shipping Temperature 25°C (ambient)
- UNSPSC CODE 41116161
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Specifications
-
Specific References
Subkhangulova A et al. (2023) Tomosyn affects dense core vesicle composition but not exocytosis in mammalian neurons Elife. 12:e85561 Species: Mouse; Application: IHC, WB
- General References Chacon-Fernandez P et al. (2016), Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor in Megakaryocytes. J Biol Chem. 2016 May 6; 291(19): 9872-9881. Species: Human. Application: WB, IF.

 1800 605-5127
1800 605-5127 +61 (0)8 8352 7711
+61 (0)8 8352 7711