Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), Chicken Polyclonal Antibody
- Product Name Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), Chicken Polyclonal Antibody
-
Product Description
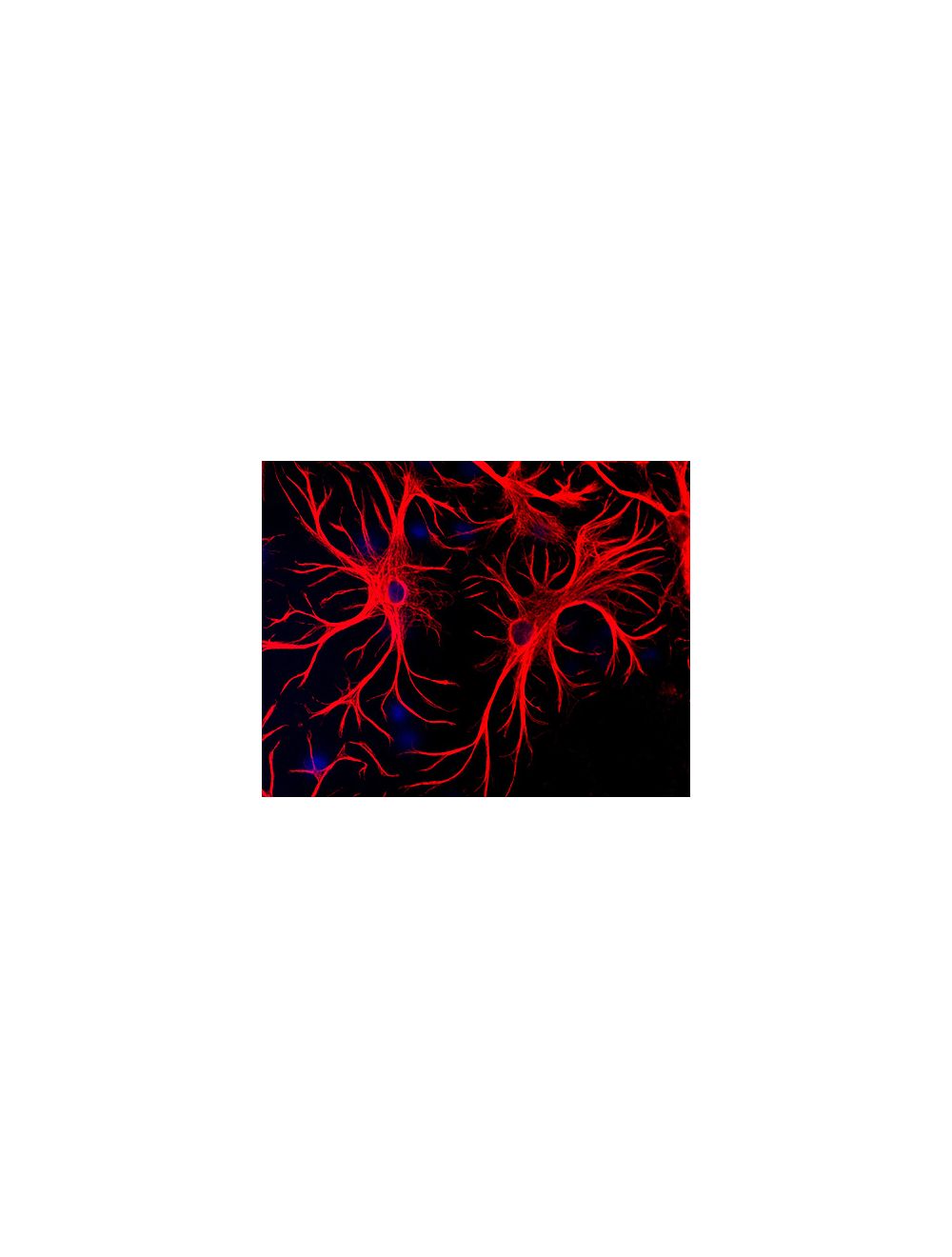
Chicken anti-Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) Polyclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for WB, IHC-Paraffin-embedded, IHC-Frozen, ICC.
- Alternative Names Astrocyte; Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GFAP;
- Application(s) ICC, IHC-Frozen, IHC-Paraffin-embedded, WB
- Antibody Host Chicken
- Antibody Type Polyclonal
- Specificity The specificity of this antibody has been confirmed by WB. Human, Rat, Mouse, Feline. Predicted to react with other mammals.
- Species Reactivity Cat, Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Rat
- Immunogen Description Recombinant GFAP (expressed in E.coli) and native bovine GFAP
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Purity Description IgY
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Product Info
-
Product Description
Chicken anti-Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) Polyclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for WB, IHC-Paraffin-embedded, IHC-Frozen, ICC.
- Application(s) ICC, IHC-Frozen, IHC-Paraffin-embedded, WB
- Application Details Western Blotting (WB), Immunocytochemistry (ICC) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC). WB: A dilution of 1:5,000 is recommended. ICC: A dilution of 1:1,000-1:5,000 using fluorescent secondary antibodies or peroxidase or other enzyme-linked methods is recommended on 4% PFA fixed cells in culture, with 3hr-o/n incubation of primary antibody. IHC: 4% PFA frozen tissues, permeabilized. IHC (paraffin-embedded): capable, HEIR treatment typically necessary. Biosensis recommends optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- Target Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)
- Specificity The specificity of this antibody has been confirmed by WB. Human, Rat, Mouse, Feline. Predicted to react with other mammals.
- Target Host Species Human
- Species Reactivity Cat, Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Rat
- Antibody Host Chicken
- Antibody Type Polyclonal
- Antibody Isotype IgY
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Immunogen Description Recombinant GFAP (expressed in E.coli) and native bovine GFAP
- Purity Description IgY
- Format Lyophilized IgY preparation, with sodium azide.
- Reconstitution Instructions Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute with 50 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material.
- Storage Instructions After reconstitution of lyophilized antibody, aliquot and store at -20°C for a higher stability. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
- Batch Number Please see item label.
- Expiration Date 12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
- Alternative Names Astrocyte; Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GFAP;
- Uniprot Number Q28115
- Uniprot Number/Name Q28115 (GFAP_BOVIN)
- Scientific Background Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is approx. 50 kDa intra-cytoplasmic filamentous protein of the cytoskeleton in astrocytes. During the development of the central nervous system, it is a cell-specific marker that distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells. GFAP immunoreactivity has been shown in immature oligodendrocytes, epiglottic cartilage, pituicytes, papillary meningiomas, myoepithelial cells of the breast and in non-CNS: Schwann cells, salivary gland neoplasms, enteric glia cells, and metastasizing renal carcinomas.
- Shipping Temperature 25°C (ambient)
- UNSPSC CODE 41116161
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Specifications
-
Specific References
Britz J et al. (2024) Sex-Dependent Effects of Chronic Circadian Disruption in AβPP/PS1 Mice J Alzheimers Dis. 97(2): 855 Application: Mouse IF
Stallings NR et al. (2023) Long-term normalization of calcineurin activity in model mice rescues Pin1 and attenuates Alzheimer’s phenotypes without blocking peripheral T cell IL-2 response Alzheimers Res Ther. 15(1):179. Application: Mouse, IHC (IF).
Hascup KN et al. (2020) Riluzole attenuates glutamatergic tone and cognitive decline in AβPP/PS1 mice. J Neurochem. [Epub ahead of print] Application: Mouse, IHC(IF). -
General References
Brenner M. et al (2001) Mutations in GFAP, encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein, are associated with Alexander disease. Nat Genet. 2001 Jan;27(1):117-20.

 1800 605-5127
1800 605-5127 +61 (0)8 8352 7711
+61 (0)8 8352 7711