Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated, (pNF-H), Chicken Polyclonal Antibody
- Product Name Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated, (pNF-H), Chicken Polyclonal Antibody
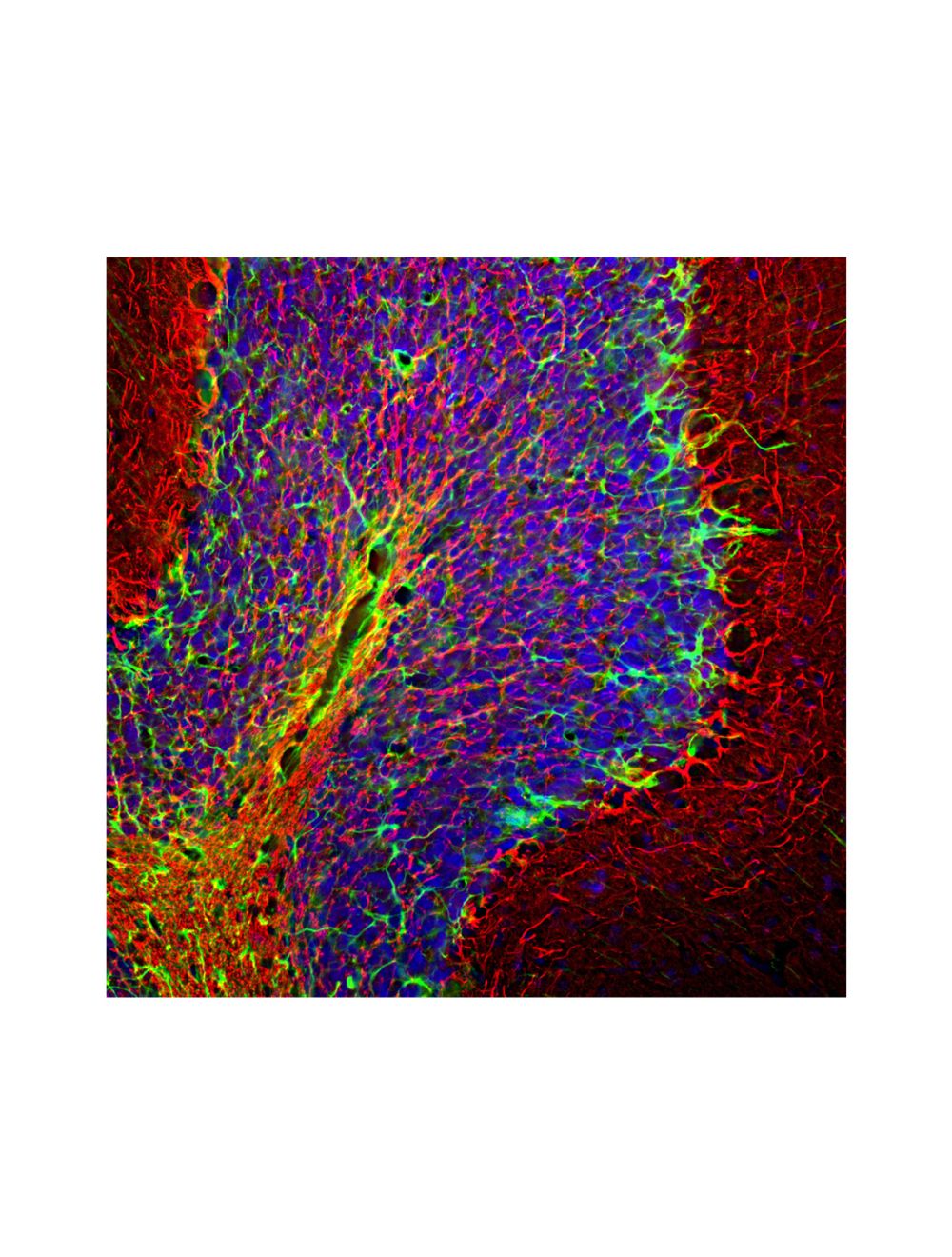
- Product Description Chicken anti-Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated, (pNF-H), Polyclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for WB, ELISA and Immunostaining.
- Alternative Names NF-H; NFH; NF-200; NF200; NF-H; NEFH; N52; Neurofilament heavy polypeptide; Neurofilament triplet H protein; 200 kDa neurofilament protein; KIAA0845
- Application(s) ELISA, IF, ICC, IHC, WB
- Antibody Host Chicken
- Antibody Type Polyclonal
- Specificity Species cross-reactivity includes human, rat, mouse, cow, pig, horse and dog. This antibody reacts with phosphorylated NF-H and is seen as a band at approx 200 kDa in WB. Refer to publication by Shaw et al (2005) for the use of this antibody in an ELISA to detect NF-H. Predicted to react with other mammalian tissues due to sequence homology.
- Species Reactivity Bovine, Dog, Horse, Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Pig, Rat
- Immunogen Description This antibody has been made against biochemically isolated NF-H purified from bovine spinal cord.
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Purity Description IgY Preparation
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Product Info
- Product Description Chicken anti-Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated, (pNF-H), Polyclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for WB, ELISA and Immunostaining.
-
Related Products
Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated, (pNF-H), Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (NAP4)
Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated, (pNF-H), Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Neurofilament Heavy, phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated (pNF-H), Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- Application(s) ELISA, IF, ICC, IHC, WB
- Application Details Western blot (WB), Immunocytochemistry (ICC) / Immunofluorescence (IF), and Immunohistochemistry (IHC). A dilution of 1:20,000-50,000 is recommended for WB. A dilution of 1:20,000 is recommended for ICC/IF and IHC. Biosensis recommends optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- Target Neurofilament heavy polypeptide, phosphorylated (pNF-H)
- Specificity Species cross-reactivity includes human, rat, mouse, cow, pig, horse and dog. This antibody reacts with phosphorylated NF-H and is seen as a band at approx 200 kDa in WB. Refer to publication by Shaw et al (2005) for the use of this antibody in an ELISA to detect NF-H. Predicted to react with other mammalian tissues due to sequence homology.
- Target Host Species Bovine
- Species Reactivity Bovine, Dog, Horse, Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Pig, Rat
- Antibody Host Chicken
- Antibody Type Polyclonal
- Antibody Isotype IgY
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Immunogen Description This antibody has been made against biochemically isolated NF-H purified from bovine spinal cord.
- Purity Description IgY Preparation
- Format Lyophilized IgY preparation, with sodium azide.
- Reconstitution Instructions Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute with 50 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material.
- Storage Instructions Store lyophilized antibody at 2-8°C After reconstitution of lyophilized antibody, aliquot and store at -20°C for a higher stability. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Store at 4°C for up to one month for short term storage and frequent use.
- Batch Number Please see item label.
- Expiration Date 12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
- Alternative Names NF-H; NFH; NF-200; NF200; NF-H; NEFH; N52; Neurofilament heavy polypeptide; Neurofilament triplet H protein; 200 kDa neurofilament protein; KIAA0845
- Uniprot Number P12036
- Uniprot Number/Name P12036 (NFH_HUMAN)
- Scientific Background Neurofilaments are the 10nm or intermediate filament proteins found specifically in neurons, and are composed predominantly of three major proteins called NF-L, NF-M and NF-H, though other filament proteins may be included also. The major function of neurofilaments is likely to control the diameter of large axons. NF-L is the neurofilament light or low molecular weight polypeptide and runs on SDS-PAGE gels at 68-70kDa with some variability across species. Antibodies to NF-L are useful for identifying neuronal cells and their processes in cell culture and sectioned material. NF-L antibody can also be useful for the visualization of neurofilament rich accumulations seen in many neurological diseases, such as Lou Gehrig’s disease (ALS), giant axon neuropathy, Charcot-Marie Tooth disease and others. (Ref: uniprot.org)
- Shipping Temperature 25°C (ambient)
- UNSPSC CODE 41116161
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Specifications
-
Specific References
Jarjour A.A. et al (2007) Maintenance of axo-oligodendroglial paranodal junctions requires DCC and netrin-1. J Neurosci. 2008 Oct 22;28(43):11003-14.
Pearse D.D. et al (2007) Transplantation of Schwann cells and/or olfactory ensheathing glia into the contused spinal cord: Survival, migration, axon association, and functional recovery. Glia. 2007 Jul;55(9):976-1000.
Shaw G. et al (2005) Hyperphosphorylated neurofilament NF-H is a serum biomarker of axonal injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Nov 4;336(4):1268-77.

 1800 605-5127
1800 605-5127 +61 (0)8 8352 7711
+61 (0)8 8352 7711