Amylo-Glo RTD Amyloid Plaque Stain Reagent
- Product Name Amylo-Glo RTD Amyloid Plaque Stain Reagent
-
Product Description
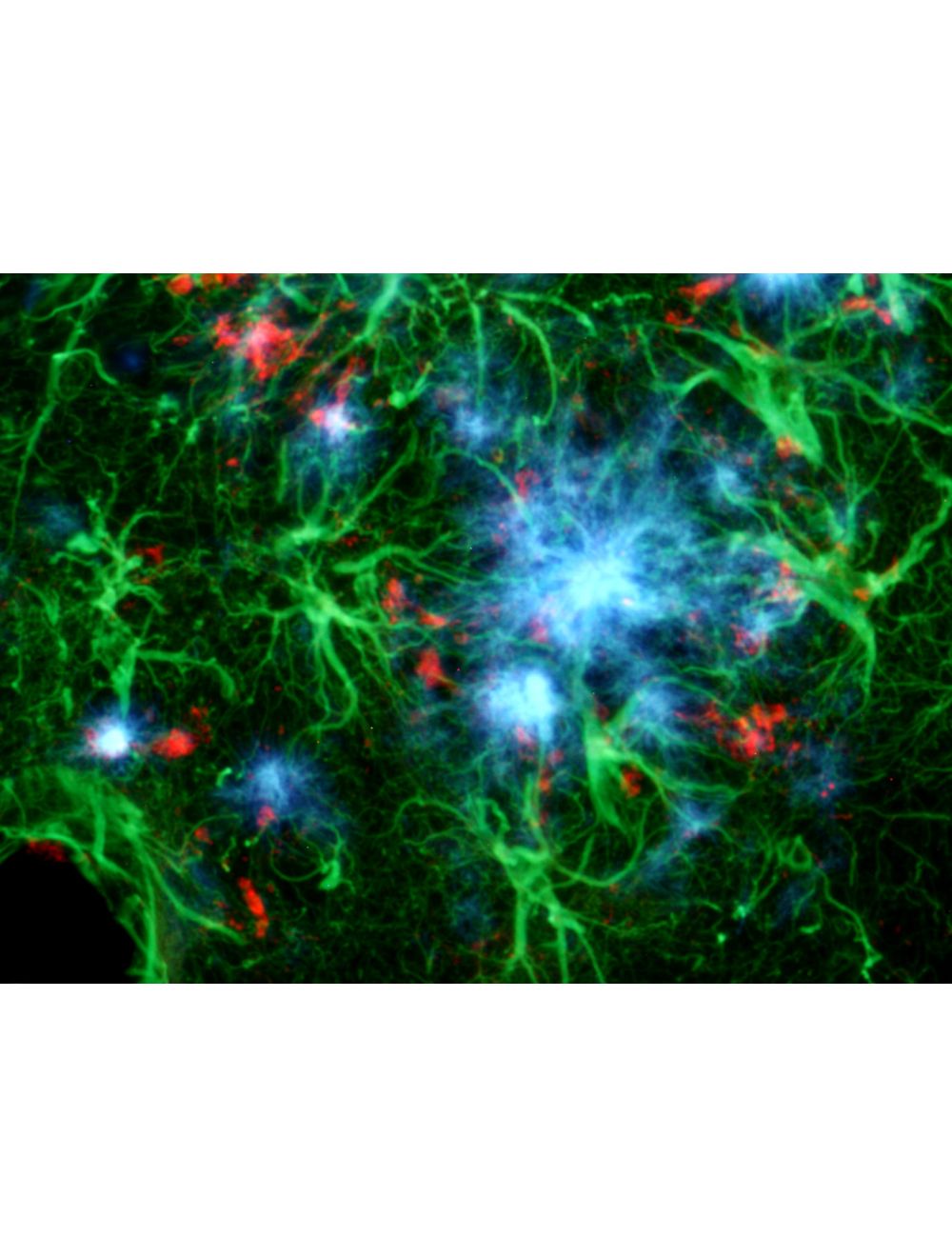
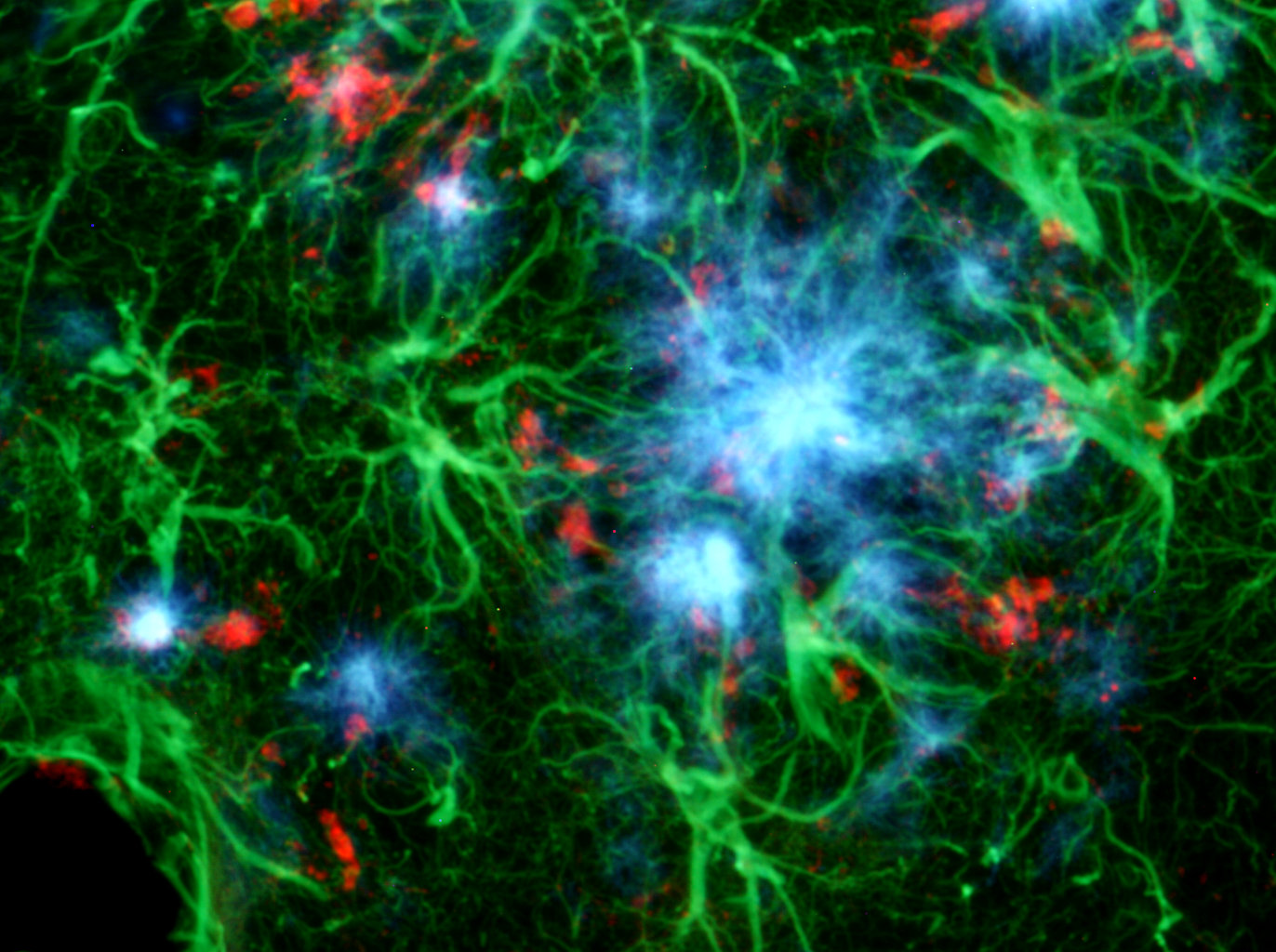
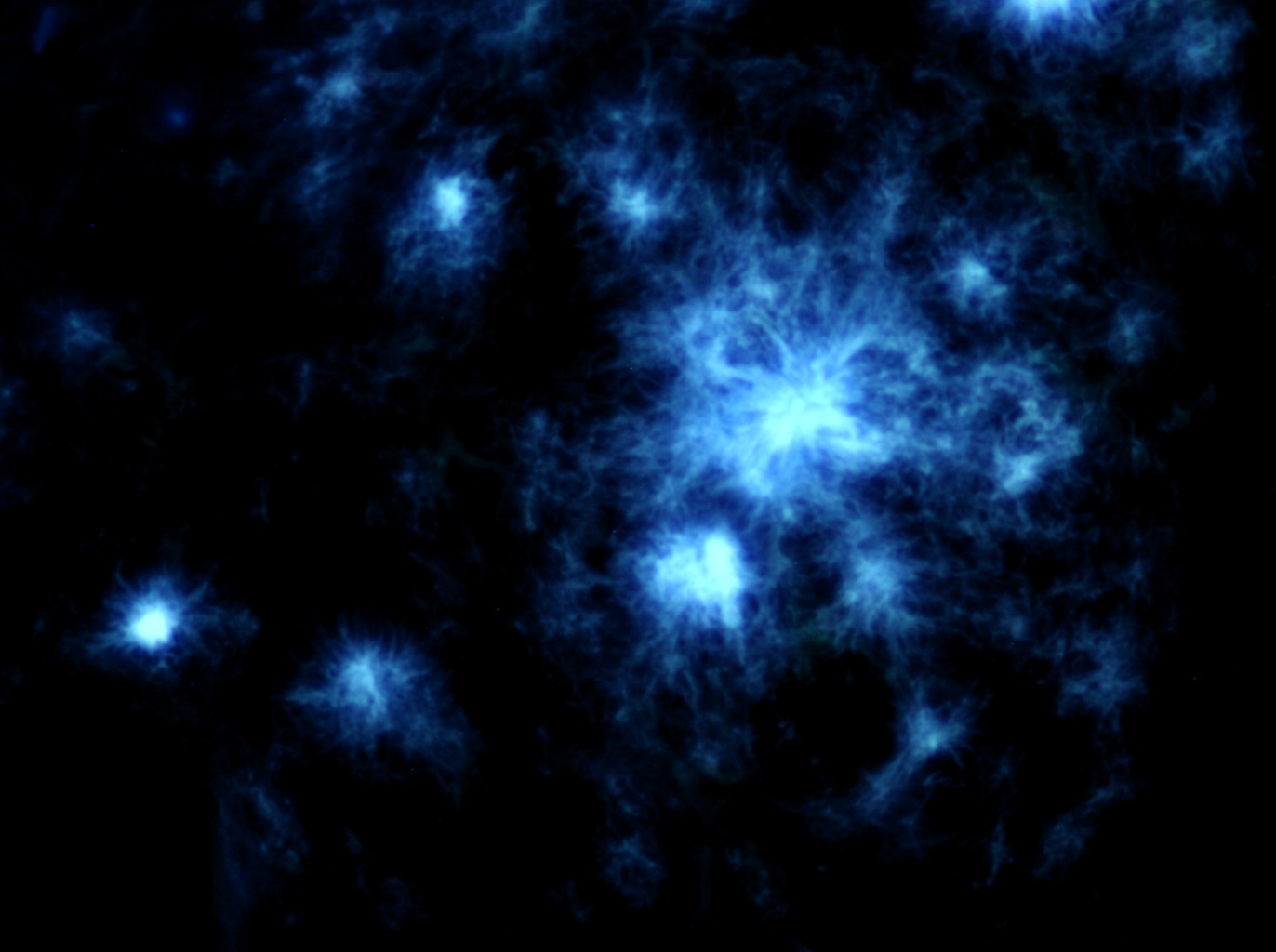
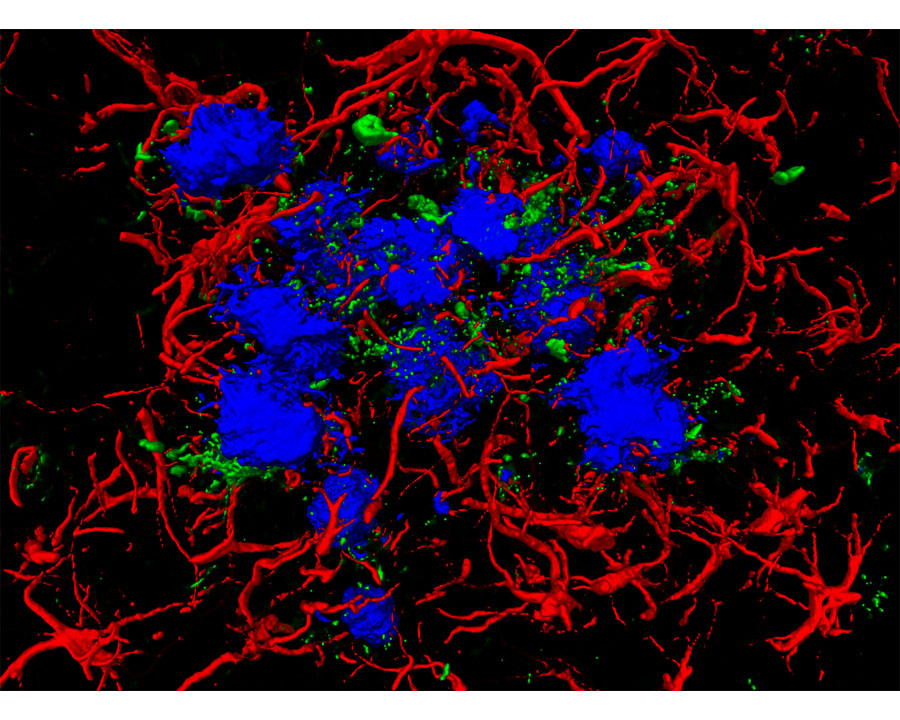
Amylo-Glo RTD Ready to Dilute Staining reagent is designed to stain amyloid plaques in tissue sections. This novel marker has several advantages over other conventional markers such as Thioflavin S and Congo Red because of its unique chemical and spectral properties. (L. Schmued et al. (2012) J.Neuroscience Methods 209:120- 126). Using Amylo-Glo results in a very bright blue UV excitable stain under physiological conditions that will not bleed through when illuminated with other filters. Its brightness makes it ideal for low magnification quantification studies, while its unique excitation/emission profile and mild staining conditions makes it ideal for combination for multiple immunofluorescent labeling studies. Amylo-Glo RTD is compatible with fresh, frozen, and formalin-fixed immunohistochemistry or cytochemistry, and it is particularly good for confocal and multiple labeling because of its high fluorescent intensity and high resistance to photo-bleaching. Moreover because Amylo-Glo fluoresces in the UV channel, double and triple labeling experiments can be performed very easily (see protocol).
- Alternative Names AmyloGlo
- Application(s) ICC, IHC-Frozen, IHC-Paraffin-embedded
- Specificity Amyloid plaques both intraneuronal and vascular
- Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Rat
- Concentration 100X
- Purity Description Thin layer chromatography using alumina plates and a solvent system of ethanol and water (3:1) revealed the presence of two fluorescent isomers. No amount of starting material was detected.
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Product Info
-
Product Description
Amylo-Glo RTD Ready to Dilute Staining reagent is designed to stain amyloid plaques in tissue sections. This novel marker has several advantages over other conventional markers such as Thioflavin S and Congo Red because of its unique chemical and spectral properties. (L. Schmued et al. (2012) J.Neuroscience Methods 209:120- 126). Using Amylo-Glo results in a very bright blue UV excitable stain under physiological conditions that will not bleed through when illuminated with other filters. Its brightness makes it ideal for low magnification quantification studies, while its unique excitation/emission profile and mild staining conditions makes it ideal for combination for multiple immunofluorescent labeling studies. Amylo-Glo RTD is compatible with fresh, frozen, and formalin-fixed immunohistochemistry or cytochemistry, and it is particularly good for confocal and multiple labeling because of its high fluorescent intensity and high resistance to photo-bleaching. Moreover because Amylo-Glo fluoresces in the UV channel, double and triple labeling experiments can be performed very easily (see protocol).
-
Related Products
Amyloid beta peptide (A-beta 40/42), Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Amylo-Glo RTD Amyloid Plaque Stain Reagent with EtBr counter stain
- Application(s) ICC, IHC-Frozen, IHC-Paraffin-embedded
- Application Details Staining of amyloid plaques in human and animal tissues, see included protocol
- Target Amyloid plaque
- Specificity Amyloid plaques both intraneuronal and vascular
- Target Host Species Species Independent
- Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Other Mammals (Predicted), Rat
- Ex/Em Max Excitation Peak: 334 nm; Emission Peak: 533 nm - unbound, 438 nm when bound to amyloid. To visualize Amylo-glo in tissue, UV light is required. For example, Amylo-Glo tissue can be examined using an epifluoresent microscope with UV (Nikon UV-2A) filter cube. Excitation (325-375 nm) Emission (400-450 nm) is typical. Also note, it is not uncommon for Amylo-Glo to appear light yellow when examined by eye, yet appear a light blue color when photographed.
- Detection Method Fluorescence
- Kit Components 5 mL of 100X Amylo-Glo RTD (A-G RTD) solution
- Purity Description Thin layer chromatography using alumina plates and a solvent system of ethanol and water (3:1) revealed the presence of two fluorescent isomers. No amount of starting material was detected.
- Format The reagents in the Amyloid Plaque Stain Reagent (100x) are all supplied in a liquid format and are ready-to-dilute.
- Concentration 100X
- Reconstitution Instructions Ready to dilute per protocol; 100X
- Storage Instructions The stock solution can be stored for up to 6 months after date of receipt at 2-8°C protected from light. No preservatives. Use sterile technique when handling and proper laboratory procedures.
- Batch Number Please see item label.
- Expiration Date 6 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
- Alternative Names AmyloGlo
- Shipping Temperature 2-8°C (on cold packs)
- UNSPSC CODE 60103920
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Specifications
-
Specific References
Tsay H et al. (2024) “Reducing brain AB burden ameliorates high-fat diet-induced fatty liver disease in APP/PS1 mice” Biomed Pharmacotherapy. [Epub ahead of print] Application: IHC. Species: Mouse
Bouin A et al. (2024) “New rabies viral resources for multi-scale neural circuit mapping” Mol Psychiatry. Online ahead of print . Application: IHC. Species: Mouse
Garcia-Augdo L et al. (2024) “BIN1K358R suppresses glial response to plaques in mouse model of Alzheimers disease” Alzheimers Dement. Online ahead of print . Application: IF. Species: Mouse
Britz J et al. (2024) Sex-Dependent Effects of Chronic Circadian Disruption in AβPP/PS1 Mice J Alzheimers Dis. 97(2): 855 Application: Mouse IF
Liu CC et al. (2023) "Cell-autonomous effects of APOE4 in restricting microglial response in brain homeostasis and Alzheimer’s disease" Nat Immunol. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
</aclass="newa">Stallings NR et al. (2023) "Long-term normalization of calcineurin activity in model mice rescues Pin1 and attenuates Alzheimer’s phenotypes without blocking peripheral T cell IL-2 response" Alzheimers Res Ther. 15(1):179.; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Hamilton H et al. (2023) "FABP7 drives an inflammatory response in human astrocytes and is upregulated in Alzheimer’s disease" Geroscience. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Jang JI et al. (2023) "Abnormal accumulation of extracellular vesicles in hippocampal dystrophic axons and regulation by the primary cilia in Alzheimer's disease" Acta Neuropathol Commun. 11(1):142; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Saha I et al. (2023) "The AAA+ chaperone VCP disaggregates Tau fibrils and generates aggregate seeds in a cellular system" Nat Commun. 10(10):182; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Tan Z et al. (2022) "Cognitively impaired aged Octodon degus recapitulate major neuropathological features of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease" Acta Neuropathol Commun. 10(10):182; Application: IHC/IF Species: Degu
Zhang H et al. (2022) "Degenerate mapping of environmental location presages deficits in object-location encoding and memory in the 5xFAD mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease" Neurobiol Dis. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Gallwitz L et al. (2022) "Cathepsin D: Analysis of its potential role as an amyloid beta degrading protease" Neurobiol Dis. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Silvin A et al. (2022) "Dual ontogeny of disease-associated microglia and disease inflammatory macrophages in aging and neurodegeneration" Immunity. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Shrader JM et al. (2022) "Distinct Brain Proteomic Signatures in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Rat Models of Hypertension and Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy" J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Rat
Zagorski K et al. (2022) "Immunogenicity of MultiTEP-Platform-Based Recombinant Protein Vaccine, PV-1950R, Targeting Three B-Cell Antigenic Determinants of Pathological α-Synuclein" Int J Mol Sci. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Shabestari SK et al. (2022) "Absence of microglia promotes diverse pathologies and early lethality in Alzheimer’s disease mice" Cell Rep. 39(11):110961; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Davis J et al. (2022) "rTg-D: A novel transgenic rat model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy Type-2." Cerebral Circulation - Cognition and Behavior [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Rat
Salvadores N et al. (2022) "Aβ oligomers trigger necroptosis-mediated neurodegeneration via microglia activation in Alzheimer's disease." Acta Neuropathol Commun. 10(1):31; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Javonillo DI et al. (2022) "Systematic Phenotyping and Characterization of the 3xTg-AD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease." Front Neurosci. 15:785276; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Hohsfield LA et al. (2022) "MAC2 is a long-lasting marker of peripheral cell infiltrates into the mouse CNS after bone marrow transplantation and coronavirus infection." Glia. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Tsay HJ et al. (2021) "EK100 and Antrodin C Improve Brain Amyloid Pathology in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice by Promoting Microglial and Perivascular Clearance Pathways." Int J Mol Sci. 22(19):10413; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Henningfield CM et al. (2021) "Microglia-specific ApoE knock-out does not alter Alzheimer's disease plaque pathogenesis or gene expression." Glia. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Da Mesquita S et al. (2021) "Meningeal lymphatics affect microglia responses and anti-Aβ immunotherapy." Nature. 593(7858):255-260; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Lauterborn JC et al. (2021) "Increased excitatory to inhibitory synaptic ratio in parietal cortex samples from individuals with Alzheimer's disease.” Nat Commun. 12(1):2603; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Kim JH et al. (2021) "Gamma subunit of complement component 8 is a neuroinflammation inhibitor." Brain. 144(2):528-552; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Claes C et al. (2021) "Plaque-associated human microglia accumulate lipid droplets in a chimeric model of Alzheimer's disease." Mol Neurodegener. 16(1):50; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Crapser JD. (2021) "Investigating microglial regulation of the extracellular matrix in health and neurodegenerative disease." PhD Thesis ; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Baglietto-Vargas D et al. (2021) "Generation of a humanized Aβ expressing mouse demonstrating aspects of Alzheimer's disease-like pathology." Nature Communications. 2(1):2421; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Mistrik M et al. (2021) "Microthermal-induced subcellular-targeted protein damage in cells on plasmonic nanosilver-modified surfaces evokes a two-phase HSP-p97/VCP response." Nature Communications. 12, Article Number 719; Application: ICC/IF Species: Human
Lemoine L et al. (2020) "Regional binding of tau and amyloid PET tracers in Down syndrome autopsy brain tissue." Mol Neurodegener. 15(1):68; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Hascup KN et al. (2020) "Riluzole attenuates glutamatergic tone and cognitive decline in AβPP/PS1 mice." J Neurochem. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Holloway OG et al. (2020) "Microglia Demonstrate Local Mixed Inflammation and a Defined Morphological Shift in an APP/PS1 Mouse Model. J Alzheimers Dis. 77(4):1765-81; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
McQuade A et al. (2020) "Gene expression and functional deficits underlie TREM2-knockout microglia responses in human models of Alzheimer s disease. Nat Commun. 11(1):5370; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Hascup KN et al. (2020) "Hippocampal alterations in glutamatergic signaling during amyloid progression in AβPP/PS1 mice." Sci Rep. 10(1):14503; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Crapser JD et al. (2020) "Microglia facilitate loss of perineuronal nets in the Alzheimer's disease brain." EBioMedicine. 58:102919; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Abe Y et al. (2020) "Behavioral and electrophysiological evidence for a neuroprotective role of aquaporin-4 in the 5xFAD transgenic mice model." Acta Neuropathol Commun. 8(1):67; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Zhu X et al. (2020) "Robust neuroinflammation and perivascular pathology in rTg-DI rats, a novel model of microvascular cerebral amyloid angiopathy." J Neuroinflammation. 17(1):78; Application: IHC/IF Species: Rat
Majewski L et al. (2020) "Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Human STIM2 and ORAI1 in Neurons Exhibit Changes in Behavior and Calcium Homeostasis but Show No Signs of Neurodegeneration." Int J Mol Sci. 21(3); Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Davtyan H et al. (2019) "Testing a MultiTEP-based combination vaccine to reduce Aβ and tau pathology in Tau22/5xFAD bigenic mice."Alzheimers Res Ther. 11(1):107; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Yeh SHH et al. (2019) "A high-sucrose diet aggravates Alzheimer's disease pathology, attenuates hypothalamic leptin signaling, and impairs food-anticipatory activity in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice."Neurbiol. Aging. [In press]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Bharani KL et al. (2019) "Serum Pro-Bdnf Levels Correlate With Phospho-Tau Staining In Alzheimer's Disease."Neurbiol. Aging. [In press]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Hovakimyan A et al. (2019) "A MultiTEP platform-based epitope vaccine targeting the phosphatase activating domain (PAD) of tau: therapeutic efficacy in PS19 mice."Sci Rep. 9(1):15455; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Hasselmann J et al. (2019) "Development of a Chimeric Model to Study and Manipulate Human Microglia In Vivo."Neuron. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Spangenberg E et al. (2019) "Sustained microglial depletion with CSF1R inhibitor impairs parenchymal plaque development in an Alzheimer's disease model."Nat Commun. 10(1):3758 (Supplementary Figure 1); Application: IHC/IF Species: Human
Eggers C et al. (2019) "Novel cannabis flavonoid, cannflavin A displays both a hormetic and neuroprotective profile against amyloid _-mediated neurotoxicity in PC12 cells: comparison with geranylated flavonoids, mimulone and diplacone."Biochem Pharmacol. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Rat
Dominguez E (2019) "Microglial Contributions to Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis." PhD Thesis, UC Irvine. Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Jovic M et al. (2019) "Short-term fish oil supplementation applied in presymptomatic stage of Alzheimer's disease enhances microglial/macrophage barrier and prevents neuritic dystrophy in parietal cortex of 5xFAD mouse model."PLoS One. 14(5):e0216726; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Collins MJ et al. (2019) "Age moderates the effects of traumatic brain injury on beta-amyloid plaque load in APP/PS1 mice."J Neurotrauma. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Shukla AK et al. (2018) "CD11a expression distinguishes infiltrating myeloid cells from plaque-associated microglia in Alzheimer's disease."Glia. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Mouse
Feng X et al. (2018) "Quantitative proteomics reveals distinct composition of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease."Alzheimers Dement. [In press]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Human, mouse
Davis J et al. (2018) "A Novel Transgenic Rat Model of Robust Cerebral Microvascular Amyloid with Prominent Vasculopathy."Am J Pathol. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IHC/IF Species: Rat
Palombo F et al. (2017) "Detection of Aβ plaque-associated astrogliosis in Alzheimer's disease brain by spectroscopic imaging and immunohistochemistry."Analyst. [Epub ahead of print]; Application: IF Species: Mouse
Abud EM (2017) "Generation of Human Microglia from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Study Innate Immunity in Neurological Diseases."PhD Thesis. 2017; Application: IF Species: Mouse
Abud EM et al. (2017) "iPSC-Derived Human Microglia-like Cells to Study Neurological Diseases."Neuron. 2017; 49(2):278-93 Application: IF Species: Mouse
Solomon IH et al. (2017) "Brain and liver pathology, amyloid deposition, and interferon responses among older HIV-positive patients in the late HAART era."BMC Infect Dis. 2017; 17(1):151 Application: IF Species: Human
Xu F et al. (2016) "Cerebral vascular amyloid seeds drive amyloid _-protein fibril assembly with a distinct anti-parallel structure."Nat Commun. 2016; 7:13527. Application: IF Species: Mouse
Katsouri L et al. (2016) "PPARγ-coactivator-1_ gene transfer reduces neuronal loss and amyloid-_ generation by reducing _-secretase in an Alzheimer's disease model ."Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016; 113(43):12292-97. Application: IF Species: Mouse
Esposito G et al. (2016) "Autologous transplantation of intestine-isolated glia cells improves neuropathology and restores cognitive deficits in _ amyloid-induced neurodegeneration."Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 22605. Application: IF Species: Rat
Marsh SE et al. (2016) "The adaptive immune system restrains Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis by modulating microglial function."Proc Natl Sci USA. Feb 16. pii: 201525466. Application: IF Species: Hu Fibrillar amyloid visualization.
Kim YH et al. (2015) "A 3D human neural cell culture system for modeling Alzheimer's disease."Nat Protoc. Jul;10(7):985-1006. Application: IF Species: Hu, Human neural stem-cell-derived three-dimensional (3D) culture system.
Nijholt DA et al. (2015) "Pregnancy Zone Protein is Increased in the Alzheimer's Disease Brain and Associates with Senile Plaques."J Alzheimer's Disease. 46(1):227-38. Application: IF Species: Hu
Kamphuis W et al. (2015) "GFAP and vimentin deficiency alters gene expression in astrocytes and microglia in wild-type mice and changes the transcriptional response of reactive glia in mouse model for Alzheimer's disease."Glia. Jun;63(6):1036-56. Application: IF Species: Mouse
Choi SH et al. (2014) "A three-dimensional human neural cell culture model of Alzheimer's disease."Nature Oct 12. doi: 10.1038/nature1380. Application: IF Species: Hu, Human neural stem-cell-derived three-dimensional (3D) culture system.
Niedowicz DM et al. (2014). "Obesity and diabetes cause cognitive dysfunction in the absence of accelerated beta-amyloid deposition in a novel murine model of mixed or vascular dementia." Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2014 Jun 10;2:64. - General References L. Schmued et al. (2012) J.Neuroscience Methods 209:120, 126

 1800 605-5127
1800 605-5127 +61 (0)8 8352 7711
+61 (0)8 8352 7711