Ubiquitin, Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- Product Name Ubiquitin, Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- Product Description Rabbit anti-Ubiquitin Polyclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for WB, ICC.
- Alternative Names RPS27A; UBA52; UBB; UBC; Polyubiquitin-B; Polyubiquitin-C;
- Application(s) ICC, WB
- Antibody Host Rabbit
- Antibody Type Polyclonal
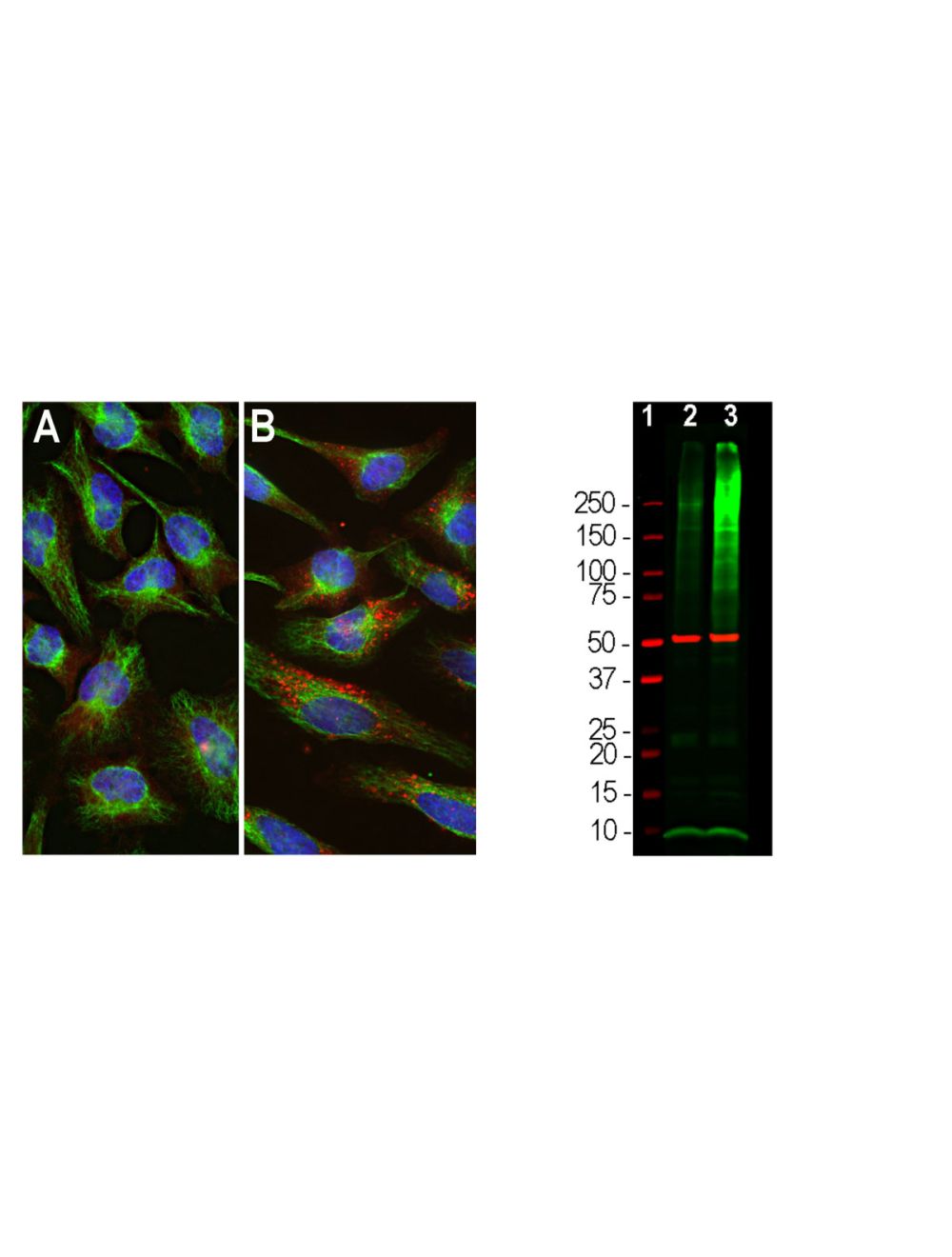
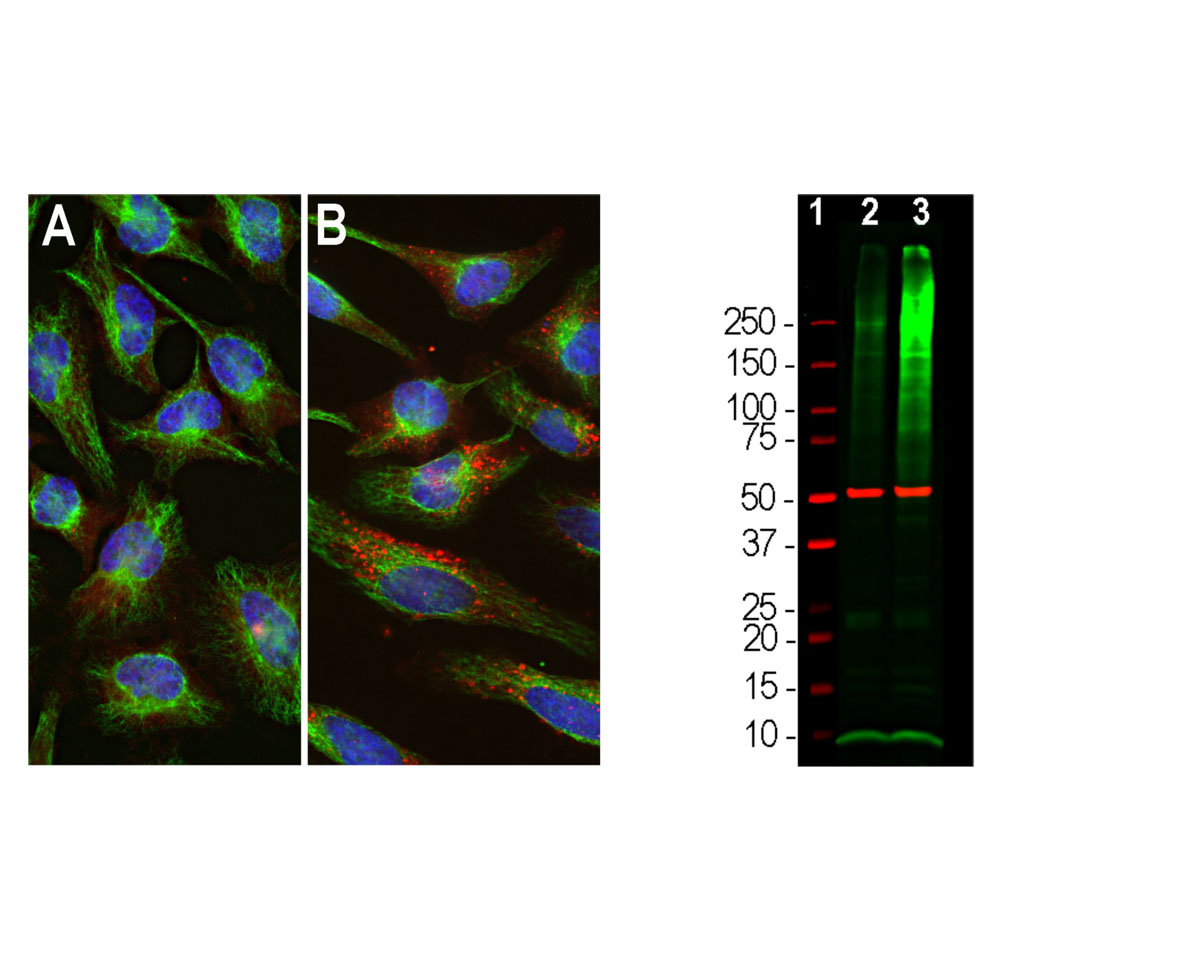
- Specificity The specificity of this antibody has been confirmed by WB. This antibody detects ~8.5 kDa Ubiquitin. Human. Predicted to react with other mammalian tissues.
- Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Rat
- Immunogen Description Glutaraldehyde cross-linked ubiquitin.
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Purity Description Whole serum
- Regulatory Status For research use only.
Product Info
- Product Description Rabbit anti-Ubiquitin Polyclonal Antibody (Unconjugated), suitable for WB, ICC.
- Application(s) ICC, WB
- Application Details Western Blotting (WB) and Immunocytochemistry (ICC). A dilution of 1:5,000 - 1:10,000 is recommended for WB. A dilution of 1:500-1,000 is recommended for ICC. Biosensis recommends optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- Target Ubiquitin
- Specificity The specificity of this antibody has been confirmed by WB. This antibody detects ~8.5 kDa Ubiquitin. Human. Predicted to react with other mammalian tissues.
- Target Host Species Human
- Species Reactivity Human, Mouse, Rat
- Antibody Host Rabbit
- Antibody Type Polyclonal
- Antibody Isotype Mixed
- Conjugate Unconjugated
- Immunogen Description Glutaraldehyde cross-linked ubiquitin.
- Purity Description Whole serum
- Format Lyophilized with sodium azide.
- Reconstitution Instructions Spin vial briefly before opening. Reconstitute with 50 µL sterile-filtered, ultrapure water. Centrifuge to remove any insoluble material.
- Storage Instructions After reconstitution of lyophilized antibody, aliquot and store at -20°C for a higher stability. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
- Batch Number Please see item label.
- Expiration Date 12 months after date of receipt (unopened vial).
- Alternative Names RPS27A; UBA52; UBB; UBC; Polyubiquitin-B; Polyubiquitin-C;
- Uniprot Number P0CG47
- Uniprot Number/Name P0CG47 (UBB_HUMAN)
- Scientific Background Ubiquitin is a highly conserved 76 amino acid protein with an estimated molecular weight of 8.56 kDa which has a central role in regulated protein degradation. It is a protein modifier which can be covalently attached to target lysines either as a monomer or as a lysine-linked polymer. Several types of polymeric chains can be formed depending on the lysine used for the assembly. Attachment to proteins as a polymer leads to their degradation by the 26S proteosome; a complex, multicatalytic cytosolic and nuclear protease. Attachment to proteins as a monomer or as an alternatively linked polymer does not lead to proteasomal degradation and may be required for numerous functions, including maintenance of chromatic structure, regulation of gene expression, stress response, ribosome biogenesis and DNA repair. Ubiquitin is synthesized as a polyubiquitin precursor with exact head to tail repeats, the number of repeats of which differ between species and strains. In some species there is a final amino-acid after the last repeat, here in bovine a Cys. Some ubiquitin genes contain a single copy of ubiquitin fused to a ribosomal protein (either L40 or S27a).
- Shipping Temperature 25°C (ambient)
- UNSPSC CODE 41116161
- Regulatory Status For research use only.

 1800 605-5127
1800 605-5127 +61 (0)8 8352 7711
+61 (0)8 8352 7711